Before those lectures, I thought software was all about the external application for systems, but totally have no idea about the different types of software. Thanks to this week’s class, which proceeds to the operating system layer, focuses on the classification of software and it helped me to have a better view on the term ‘software’.
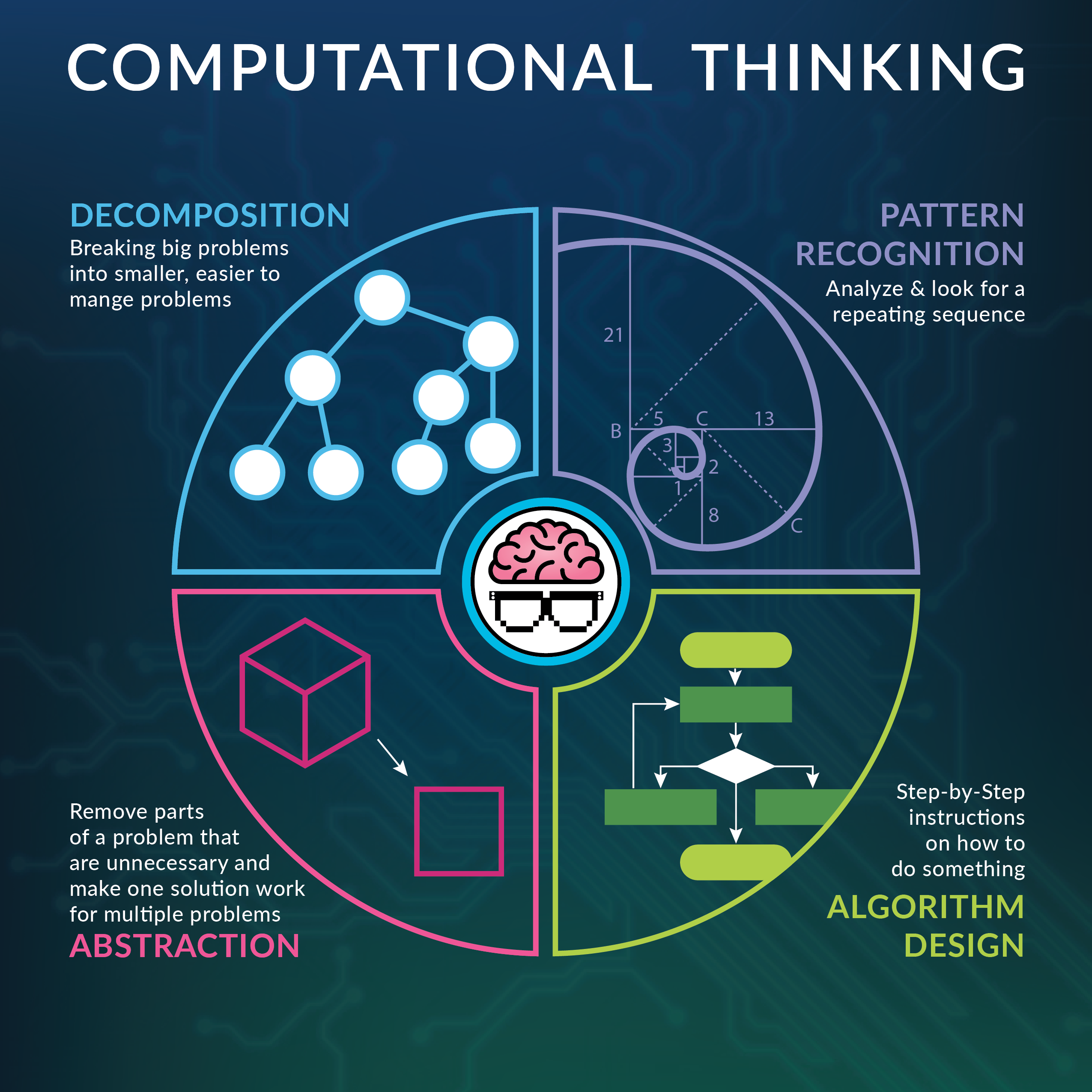
- Hierarchy of software
Software can be further categorized as two distinct types, system software and application software, in which they are used for different purposes, as the name suggests. In class, we did some activities to try to memorize this hierarchy graph, because it is really essential for learning software. The graph of the hierarchy is shown below.

- System software
System software is a type of computer program that is designed to run a computer’s hardware and application programs. This can be understood as the interface between hardware and user applications. This can be broken down into four smaller categories, operating system software, utility software, library programs and translator software.
Operating system is the combination of different programs that makes computer usable and convenient for the users. It is an interface between the application software and computer, so that without operating system, all the applications won’t be able to function normally. Some examples of operating system include Windows, Linux, Mac OS.

Utility software is usually used to maintain the smooth function of the operating system and it does not occupy much memory or CPU. For instance, virus detector (Avast), temperature monitor (Macs fan control) and as well as searching engine in the operation system (Alfred). Those examples are the one that we presented in class activities, everyone stood up to give some examples of utility software, some examples presented by classmates are activity monitor and unarchiver.

A library program is a collection of functions that can be used by other programs. It contains code and data to provide services, for instance printing, graphic engines. One specific example can be the Microsoft office, which all of their sub-applications are all looking the ‘same’ because it’s using the same interface.
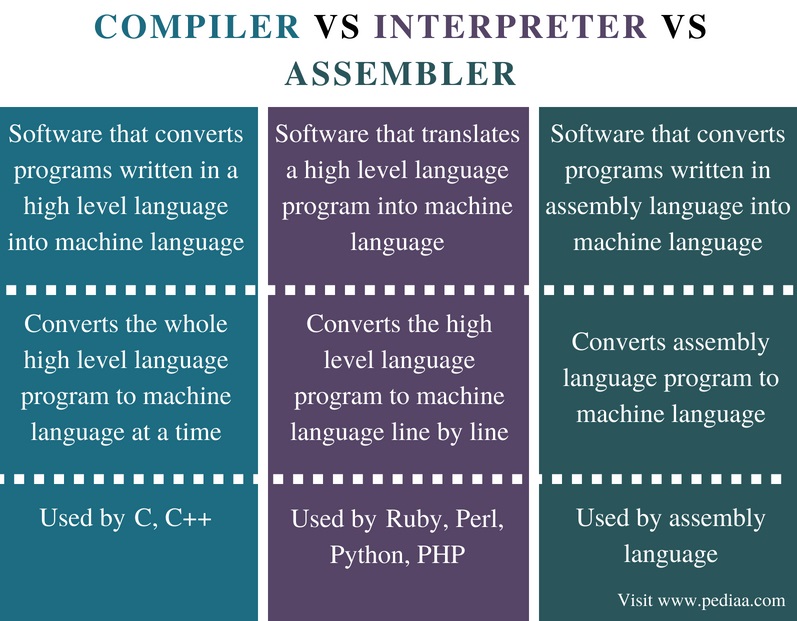
Translator software, allows new programs to be written and run on the computer by converting the source code in to machine code. There are normally three types, assembler, compiler and interpreter.
Assembler is used to translate the assembly language program into machine code. The assembly language program is the low-level program. Compiler is a program that takes a program in a high-level language (e.g. python, java, c++), the source code, and translates it into object code all at once. Interpreter analyses and executes each line of a high-level language program one line at a time.
- Youtube video
In class, we watched a video in regards to interpreter and compiler, the interpreter is used to ‘translate’ the instruction one by one. The process is slow, but it does have a chance to correct the mistakes in translation. Compiler, on the other hand, compiles the information together. It run much quicker, but does require a preparation time.
- Application software
This kind of software allows user to perform non-computer tasks, which means that users use these types of applications for writing a document, making a poster, etc. And this can be further divided into general purpose application software, special purpose application software and bespoke application software.
General purpose application software, as the name suggests, can do multiply tasks, not only limited to single function. For instance, the Office word, users can use it for different purposes, like writing essay, making poster, or creating tables. Special purpose application, however, focuses on a specific function, like calculators, web browsers. Bespoke applications are those that are specifically designed for users or purposes. For instance, I’ve built a program for the automatic robot this year together with a professor, the program is specifically suited to the robot, which connects to its cameras and wheels. Other examples are software for medical uses, or for the military.



- Flowchart poster
We choose the topic that kind of reflect IB students’ daily life, that is ‘When to do homework?”. We design the flowchart first, consider about the common situation in our daily life, and then finish up the pseudocode according to the flowchart. Here is our poster.

So in a word, this week focuses on the smaller categories of software, and it would be really helpful for me to identify those different applications in the future.