In this week’s classes, we learned what is inside a computer to see how it works by going deep into the role of CPU and the binary system. To understand that better, we did two roleplaying activities to imitate how the CPU and the binary number system work. We also practiced how to convert binary to and from decimal.
- Functions of CPU, CU, ALU, Register, and Bus
CPU stands for the Central Processing Unit which is like the brain of a computer. It fetches the instructions from the memory and calculates and processes the instruction later. As for CU, refers to the Control Unit, directs operation of the processor. It tells the computer’s memory, arithmetic/logic unit and input and output devices how to respond to a program’s instructions.ALU refers Arithmetic Logic Unit which does the calculations (arithmetic) and deals with logic in a computer by passing through different logic gates. The Register functions as a memory storage location within a CPU but it is different from the secondary storage because it can only store the information temporarily. The information will be all cleared once the computer is shut down. The Bus serves as the ‘transporter’ of messages by carring the information to communicate with other parts of the CPU.
- How does a computer work
After learning the IPO model and the CPU, I kind of have a clearer view on how the computer works. As soon as the computer receives the instruction from the user,the subsystem sends a message to the CPU to process it. The CPU would fetch and execute these instructions from memory. Within the CPU, CU fetches information from the Register and memory and tells ALU what to do through the Bus. After ALU has done its calculations, it would send the result by the Bus to display it on your screen as the output.For instance, there are two variables and you give the instruction ‘x+3, y+4’ to the computer. The computer receives the command and directly gives it to the CPU. The CU fetches the information from the Register, and the Bus will collect the data and send the information to the ALU. After the ALU done the calculations—plus 3 to x and plus 4 to y, the bus will again carry the result to the display part. Finally, the output will be shown on the screen by display.

- Binary number system
For two confusing terms, data and information. Data is raw, unorganized facts that need to be processed. It can be known as the ‘raw material’ for a computer to process. However, when data is processed, organized, structured or presented in a given context, it is then called information.
| Comparison between Data&Information | |
| Data | Information |
| Raw material | Product |
| Input | Output |
| Doesn’t carry a meaning | Carries a logical meaning |
The computers won’t use the human language, due to the fact that it is waste of their storage and time, so computers use binary number system to represent the data and process it. Binary number system expresses number with only 2 symbols: 1 and 0.
- How to Convert Binary to Decimal
- Write down the binary number
- List the powers of two from right to left
- Write the digits of the binary number below their corresponding powers
- Add the powers which have number “1” below them
- The final answer is the decimal way to express the binary number
For example, for binary number 111011:
| 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 |
| 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
As there is the number “1” below 32, 16, 8, 2 and 1, we add them together: 32+16+8+2+1=59, which 59 is the decimal way to express 111011.
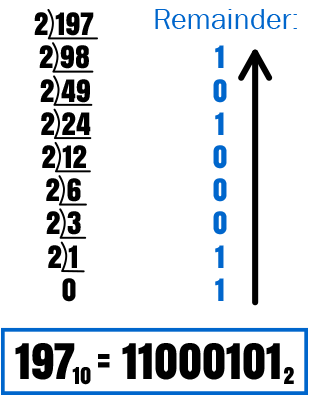
- How to convert Decimal from Binary (Short Division)
- Divide the decimal number by 2
- Record the remainder from Step 1 as the rightmost digit.
- Divide the quotient of the previous by 2
- Repeat Step 3 and Step 4, record remainders from right to left, until the quotient becomes less than 2.
- Read the remainder from bottom to top
- Roleplaying activities
We did two roleplay activities in regard to CPU and binary system. In the first activity, we learn about how the computer represent different numbers by 0 and 1. We learned how dots can represent a number as the binary number system can do by using cards with 1,2,4,8…dots on it. Then we flipped the dots cards to represent numbers from 1 to 20 with our partners. This activity helped me to learn the system of binary representation.

In the second roleplaying activity, 5 people together as a group plays different components of the CPU to intimate the process that how it works. I was the ALU (Arithmetic and logic unit) in this activity, what I do is to receive the instructions transported by BUS from the Register and do the calculations, then give the results to the BUS and the BUS will then pass it to the display. Before this activity, I was still messed up with the logic behind CPU and still being confused about the flow of information in CPU. This activity helped me to get a deeper understanding of the function for each of the component of CPU.
- ASCII and UNICODE research
ASCII, American Standard Code for Information Interchange is the old version of representations of characters. The ASCII give each letter (Upper and Lower case) and also punctuations distinct numbers to represent, from 0-127. The computer processes those numbers and them decode them back to the characters. Because I am learning Python right now, so I did some trials in the terminal of MAC and the following image is the results that represent some examples of the ASCII character representations.


The problem is, ASCII is only able to encode 128 characters into 7-bit integers, but there are millions and billions of other characters can’t be represented by ASCII. As a result, a computer from the US won’t be able to ‘communicate’ with the one from Asia.
So later on, people invented Unicode to solve this issue. Unicode is the universal code for millions of different characters and hundreds of different character sets. It is able to store characters and emoji from various languages, thus having no trouble for the computer to understand.

In conclusion, we got in touch with the computer ‘language’ this week—the binary system, as well as the brain of computer—the CPU. For me, I think learning Python would really help me to get a deeper understanding of the ASCII and UNICODE system because like Python3, all of the strings are in the UNICODE format and all of the programming are related to those character representation. It’s hard for me at this age to understand all the knowledge behind each of these terms, but I’ll still challenge myself in future courses!
Citation
- wikiHow. “How to Convert from Binary to Decimal.” WikiHow, WikiHow, 29 Mar. 2018, http://www.wikihow.com/Convert-from-Binary-to-Decimal.
- wikiHow. “How to Convert from Decimal to Binary.” WikiHow, WikiHow, 14 May. 2018, http://www.wikihow.com/Convert-from-Decimal-to-Binary.
- Torres, Gabriel. “How a CPU Works.” Hardware Secrets, 4 Oct. 2018, http://www.hardwaresecrets.com/how-a-cpu-works/.
